Difference between revisions of "Roles and Security Settings"
(→See Also) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
By setting a default user role in your [[Personal Settings|personal settings]], the system will assume that you are adding someone using a specific role when you add a new person to the system. | By setting a default user role in your [[Personal Settings|personal settings]], the system will assume that you are adding someone using a specific role when you add a new person to the system. | ||
| − | ==Advantages of Role-Based Security | + | [[User Role|User roles]] organize (group) users and, in conjunction with these permissions and other logic, control what people can see and do in their [[SmartSimple]] [[instance]]. User Roles group similar people together and are additive; this means that a user may possess multiple roles, so roles need not be mutually exclusive. Typically, we will group users on what they will be doing within [[SmartSimple]] - for example, '''Reviewers, ''''''Grant Approvers '''- and by their department - for example, '''Human Resources '''or '''Accounting. '''A [[User|user]]'s [[User Role|role]] is there fundamental to their '''Role Base Access Control (RBAC), '''which comprises what we can apply the umbrella term of '''Role-Based Security.''' |
| + | |||
| + | ==Advantages of Role-Based Security== | ||
* You can make individuals, regardless of their [[organization]], members of a role and therefore provide them access to a specific resource. | * You can make individuals, regardless of their [[organization]], members of a role and therefore provide them access to a specific resource. | ||
* When you move the user to another organization, it does not affect their permission to access a resource. | * When you move the user to another organization, it does not affect their permission to access a resource. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 20: | ||
=Configuration - Essentials= | =Configuration - Essentials= | ||
| − | |||
==Accessing Roles and Security Settings== | ==Accessing Roles and Security Settings== | ||
| − | |||
The '''Roles and Security Settings''' of your [[SmartSimple]] [[instance]] can be accessed through the following steps: | The '''Roles and Security Settings''' of your [[SmartSimple]] [[instance]] can be accessed through the following steps: | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 2 July 2019
Contents
Overview
Role-Based Security is a method of permissioning accessibility and security measures in your SmartSimple copy based on the role that is associated with the user.
With this scheme, you first create one or more roles, then associate each user with one or more of these roles.
- Note: The system will always default to the minimum level of access; be aware of this when associating a user with multiple roles.
By setting a default user role in your personal settings, the system will assume that you are adding someone using a specific role when you add a new person to the system.
User roles organize (group) users and, in conjunction with these permissions and other logic, control what people can see and do in their SmartSimple instance. User Roles group similar people together and are additive; this means that a user may possess multiple roles, so roles need not be mutually exclusive. Typically, we will group users on what they will be doing within SmartSimple - for example, 'Reviewers, 'Grant Approvers - and by their department - for example, Human Resources or Accounting. A user's role is there fundamental to their Role Base Access Control (RBAC), which comprises what we can apply the umbrella term of Role-Based Security.
Advantages of Role-Based Security
- You can make individuals, regardless of their organization, members of a role and therefore provide them access to a specific resource.
- When you move the user to another organization, it does not affect their permission to access a resource.
- Associating the role with the resource is less time-consuming than if the alternative is to associate the resource to many organizations.
This security scheme should be used when the relationships between users and system resources are more complex, and you need to provide access to resources independent of any organizational structure.
The Roles and Security Settings part of the SmartSimple system will allow you to configure the Role-Based Security scheme to your personal needs.
Configuration - Essentials
Accessing Roles and Security Settings
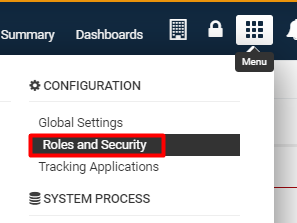
The Roles and Security Settings of your SmartSimple instance can be accessed through the following steps:
1. Click the 9-square menu icon on the top right of your page.
2. Under the heading Configuration, select Roles and Security Settings.
The Roles and Security Settings page will be displayed.
Functions of Roles and Security Settings
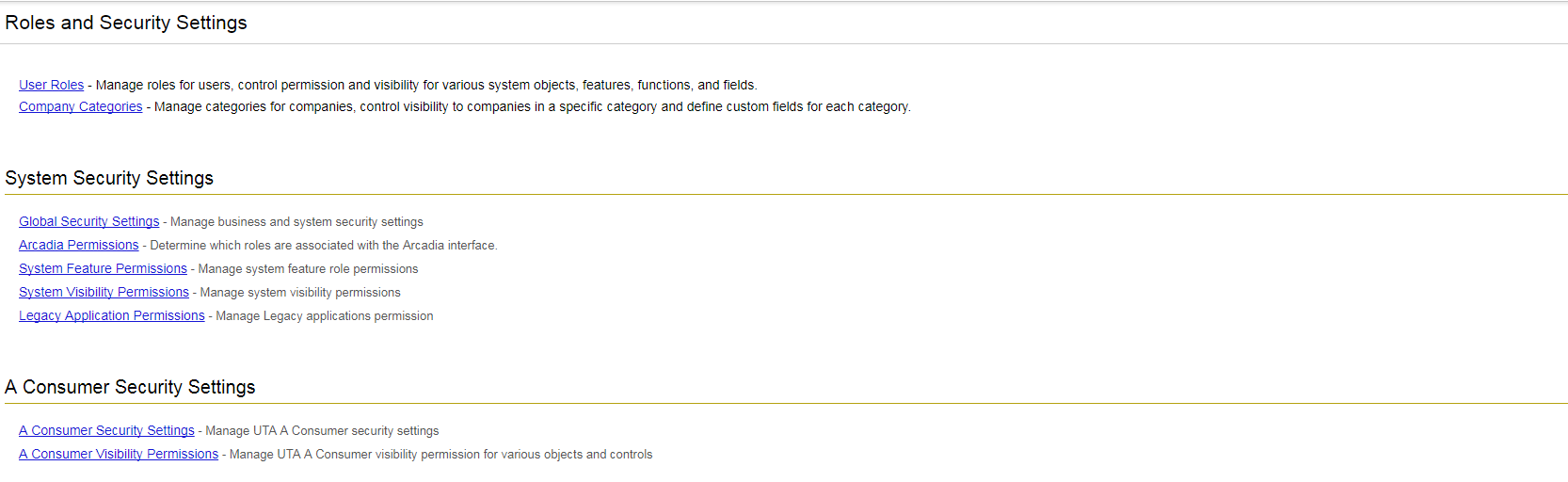
The Roles and Security Settings page allows access to the following configuration pages within SmartSimple:
| Roles and Categories |
User Roles - Use roles in order to control the menu, portal, reports, and fields associated with a specific group of users or contacts. Roles also control field visibility and the types of contacts that a user in a specific role is able to add into the system. It is under this tab that you are also able to edit the Common Portal, the aggregated portal that can be helpfully applied to users in all roles rather than a specific role.
|
| System Security Settings |
Security Settings - Manage business and system security settings, including Password Policy and Email & Email Broadcast Security. Arcadia Permissions - Determine which roles are associated with the Arcadia Interface, and if necessary, permission some roles to be able to switch to the Classic Interface (now deprecated as of November 2018 upgrade). System Feature Permissions - Allows for System Administrators to personalize their copy of SmartSimple, making various system objects available to users in different roles. The Feature permissions will allow you to modify the accessibility of certain system features, such as Notes, Reports, SmartFolders, and more. System Visibility Permissions - Allows for System Administrators to personalize their copy of SmartSimple, making various system objects available to users in different roles. In the Visibility permissions, you can limit View Access and hide certain features. Legacy Application Permissions - Determine which roles are associated with base application functions - for example, Applicant Tracking and Web Forms. |
| -based Settings |
UTA Security Settings - Permission the security settings of the specific UTA here. Features of security include a Security Matrix and role restrictions. UTA Visibility Settings - Determine the visibility permissions for various objects and level of control for the specific UTA.
|