Difference between revisions of "Custom Field Type: Special - Advanced Data Table"
(→General Settings) |
m (DWan moved page Custom Field Type: Special – XML Data to Special - Advanced Data Table over redirect) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 13:06, 13 August 2018
Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 Configuration - Essentials
- 3 Configuration - Advanced
- 3.1 Creating formulas (calculations) in XML cells
- 3.2 Adding a formula to a XML cell (working with data in the same section)
- 3.3 Adding a formula to a XML cell (working with data in the different sections)
- 3.4 Validate XML values when saving the worksheet
- 3.5 Validating values when saving record (SmartCheck, Submit Logic, Browser Script)
- 3.6 Managing Level 2 / 3 Activities with an XML Section
- 4 Displaying XML Data
- 5 Appendix
Overview
This field type can be used to create worksheets or tables such as budget sheets, and lists of information. A wide range of complexity is supported from very simple tables to multi-section, multi-year budgets. This is accomplished through the ability to configure sub-sections within the same worksheet, and also define automatic cell calculations. This all adds up to a very robust, and flexible field.
By default, the data for this field is stored in the structured XML (Extensible Markup Language) format. However, you also have the option to instead use this field as a presentation layer for lists of sub-activity records. For example, you may use this field on a UTA Level 1 record to display any associated UTA Level 2 records for a user to easily update the activities or create new activities.
If you are looking to create a basic list or budget, you can also use the field called Special - In-Line Data Grid.
| Summary | |
| Commonly Used in Markets (Philanthropy, Research, Insurance) | All |
| Used By (User Type) | All |
| Requires Administrator Setup | Yes |
| Configuration Complexity (Low, Medium, High) | High |
| Time to Configure (Minutes, Hours, Days) | Hours |
Configuration - Essentials
Creating the field
Typically XML Data custom fields are created for UTA level 1, 2 or 3, (e.g. a grant application) or they are created for organizations. To create the field:
- Navigate to the desired settings area where you want to create a worksheet (e.g. the UTA level 1).
- Click the New Field (+) button.
- For Field Type select Special - XML Data.
- Enter a Field Name and Save.
- Use the Section Builder button to begin process of creating the XML tables.
- Use the Custom Field button to navigate back from the Section Builder to the Field settings to configure the display of tables.
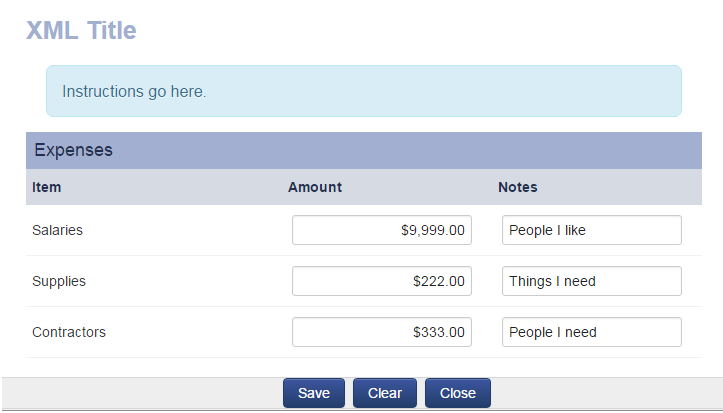
Create a Simple Table
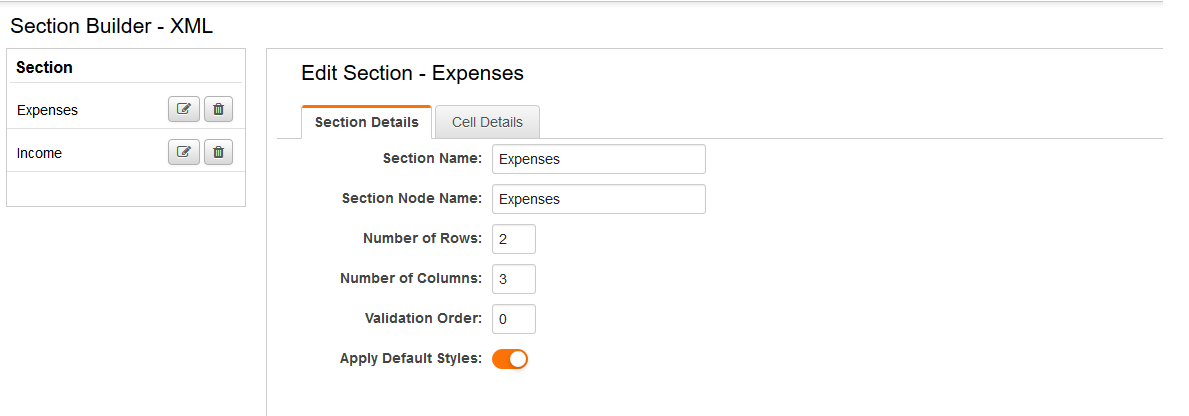
Using the XML Section Builder you can create sections and define the attributes of each section and the cells within them. You can define the number of rows and columns, the display format, calculation formulas, and style your XML.
- While editing the custom field click on the Section Builder button (the four square icon) in the action bar.
- Create a New section and enter a Section Name (e.g. Expenses).
- Enter Number of Rows and Number of Columns desired.
- Once you Save you will be brought to the Cell Details tab.
- Define a Display Name for each of the row and column headers.
- Within each of the column headers you can define a Format for the column (e.g. plain text, currency, date). For numeric formats you may also specify a precision.
- Note: to avoid confusion it is recommended to use unique node names of sections, rows, and columns within the field.
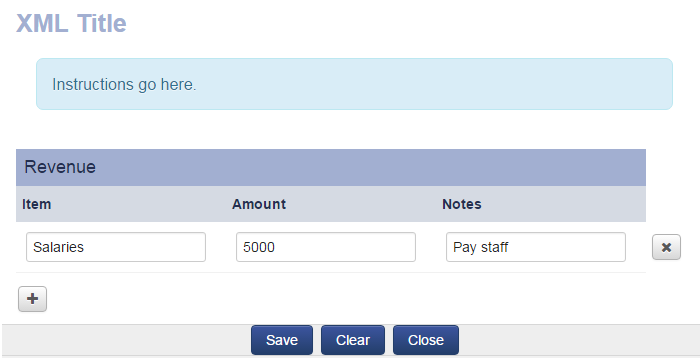
Create a Table with a Dynamic Number of Rows
In addition to defining a set number of columns and rows, you can also configure a section to handle a dynamic number of rows. The user entering the data can add rows as necessary at time of entry. This is done by entering 0 for the Number of Rows, which in turn exposes the following configuration options:
- Maximum Number of Rows: Set a maximum limit to the number of rows that can be entered, or leave as 0 for no limit.
- Maximum Message: The message to be displayed when the maximum limit is set and reached by a user. A default message is displayed if left blank.
Setting the Number of Rows to 0 also exposes the following configuration options for each column header within the Cell Details tab:
- Has Total: Display the total sum of a column.
- Total Row Label: For columns without a total display this option allows you to enter a label for the total sum of another column. For example, if column 3 was displaying a total, then you could configure the Total Row Label of column 2 to display 'Total'.
Configure the Display of Tables
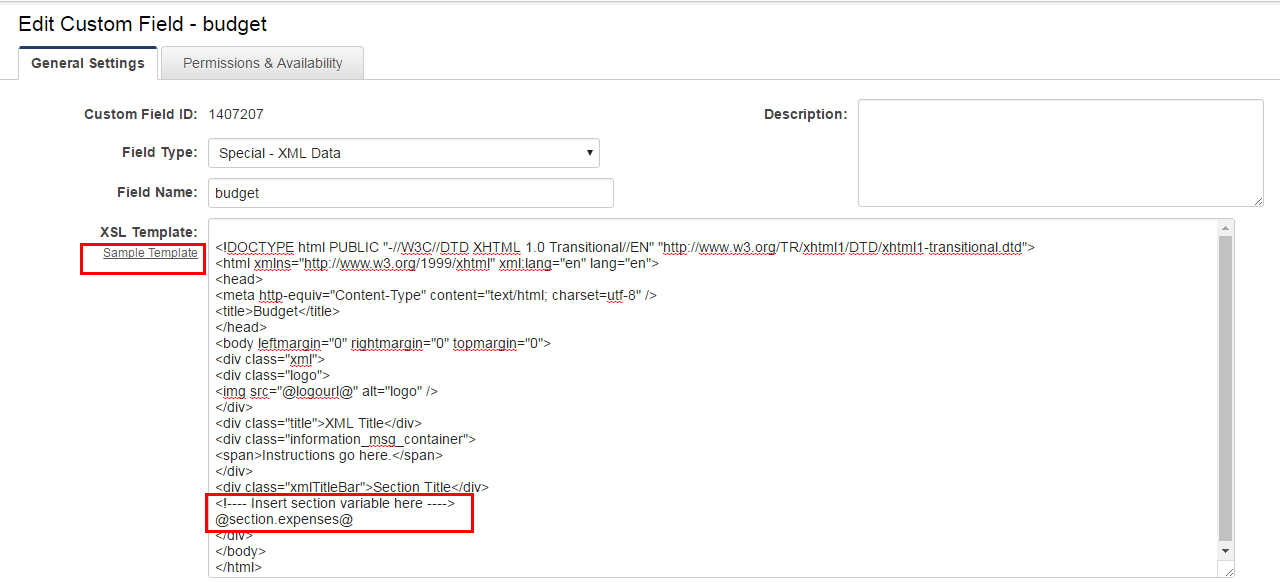
The presentation of the XML Data custom field is configured in the general settings page of the field. This is defined in the XSL Template (Extensible Style Sheet Language) option. The XSL Template includes a sample template option. Once you have inserted sample template you will need to specify which sections should appear and where they should appear.
- While editing the custom field locate the XSL Template option and insert the Sample Template.
- Locate the below marker.
<!---- Insert section variable here ---->
- Below the marker, insert variable references to the each section with the following syntax (e.g. @section.Expenses@) in the order in which you wish the sections to appear. Note: the section node name is case sensitive.
@section.SectionNodeName@
Configuration - Advanced
Creating formulas (calculations) in XML cells
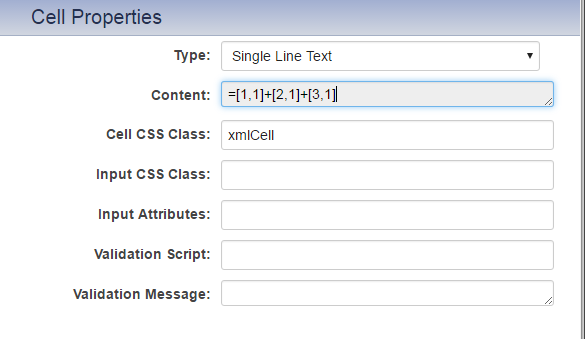
In the section builder you declare the formatting such as currency or numeric for specific columns as well as settings like precision. If you are collecting numeric or currency data you will likely want to do calculations on this information found within your XML (e.g. to sum the contents of column one, over two rows, enter =[1,1]+[2,1]).
Adding a formula to a XML cell (working with data in the same section)
- Navigate to your XML custom field.
- Click the Section Builder button in the action bar.
- Click the desired Section.
- Click the desired Cell.
- Under Cell Properties enter your desired formula into the Content input.
- Click Build.
The Syntax for basic calculations within a section:
| Operation | Symbol | Example |
| Add | + | =[row#,column#]+[row#,column#] |
| Subtract | - | =[row#,column#]-[row#,column#] |
| Divide | / | =[row#,column#]/[row#,column#] |
| Multiply | * | =[row#,column#]*[row#,column#] |
Adding a formula to a XML cell (working with data in the different sections)
Refer to cells in different sections using this syntax
[@section.sectionname.id@_rownodename_columnnodename]
e.g. =[@section.expense.id@_Total_Amount]-[@section.income.id@_Existing-funds_Amount]
Validate XML values when saving the worksheet
Clicking on a cell inside the section builder will present you with the cell properties. There are two cell properties used for the validation of cells when the xml worksheet is saved.
- Validation Script: Validates the input field.
- Validation Message: Content that is displayed, when the validation script is not true (e.g. Value must be greater than 100).
Examples
- Total Amount greater than 0, for currency formatted column totals
ssParseNum([this])>0
Message: Total must be greater than $0.00
- Date is at least 30 days in the future
datediff(ConvertDateStr([this],'@dateformat@'),'@date(currentdate)@','d') > 30
Message: Please select a date that is at least thirty 30 days from today.
- Cell is not empty
[this].length>0
Message: Please provide a value.
- Check the user selected something other than the default Combo Box value
[this]!="Default Combo Box Value"
Message: Please select a value. Note, Default Combo Box Value should be substituted with the default value you have configured, e.g. --- Select One ---.
- Integer greater than 0 (Allow only an integer or if your field on the XML is formatted to display/use a comma.)
parseInt([this])>0
Message: Please provide a numeric value greater than 0.
Validating values when saving record (SmartCheck, Submit Logic, Browser Script)
In addition to validating values when you save the XML worksheet you can also validate the XML worksheet when you save the record (e.g. save a level 1 grant application).
When creating validation for an XML custom field use the Appear Mandatory option. Appear mandatory does not enforce the validation but will make the field look mandatory (add the asterisk and color) just like the mandatory option. Once you have checked Appear Mandatory, validate the XML worksheet using one of the following validation methods, when the record is saved.
SmartCheck Validation
Use SmartCheck for XML validation when possible. SmartCheck validation is a secure server side method. SmartCheck also displays all error messages in a context as well as in one central place.
Validate an XML table node is not empty and display a message.
if("<ssEscape>@level1.xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnnodename.nodevalue@</ssEscape>"=="")
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('xml_@fieldname.id@','YourAlertMessage'); }
Submit Logic Validation
Use Submit Logic in conjunction with Submit Buttons to Validate a XML worksheet.
Check an XML node in not blank when saving the XML worksheet.
"<ssEscape>@level1.xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnnodename.nodevalue@</ssEscape>"!=""
Special - Browser Script validation
You can enter JavaScript and jQuery into XML JavaScript Function input to create specific validations. Use the following syntax when referencing a value in your variables.
@xml.customfieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnnodename@
The following function allows you to check for an already selected value from an existing row when using dynamic rows:
// REPLACE '7172_dsItem_Population' AND '7172_dsItem_Population_' WITH SPECIFIC XML FIELD ID
var saveFunc=saveXML;
saveXML=function() {
checkdupeval();
}
function checkdupeval() {
var result = 0;
var numOfRows = document.getElementsByName('7172_dsItem_Population'); //section node
var ctr=1;
for (ctr=1;ctr<numOfRows.length;ctr++)
{
var field1='7172_dsItem_Population_'+ctr;
var lastfield='7172_dsItem_Population_'+numOfRows.length;
var a = document.getElementById(field1).value;
var b = document.getElementById(lastfield).value;
if( a == b)
{
alert ("Please list each population no more than once.");
result = 1;
}
}
if(result==0)
saveFunc();
}
Managing Level 2 / 3 Activities with an XML Section
System administrators can configure XML fields to add, modify or delete Level 2 records on a Level 1 entity or Level 3 records on a Level 2 entity.
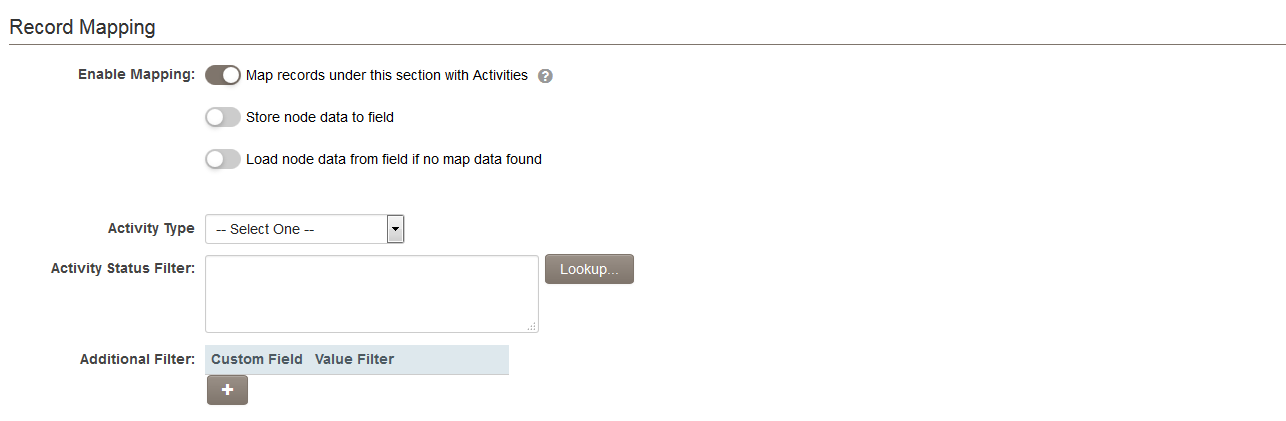
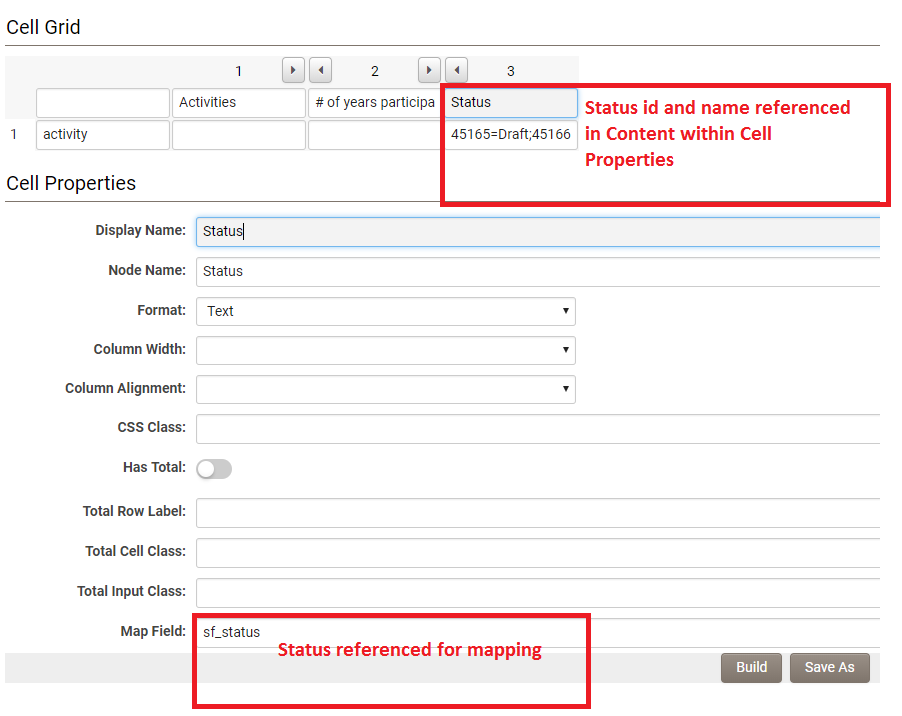
In the XML Section Builder, when the Number of Rows for a Section is set to '0', the Enable Mapping option will be shown.
When Enable Mapping is selected, you can choose one type of activities to be referenced by the XML field.
The Activity Status Filter setting allows you to filter the activities to be referenced by status.
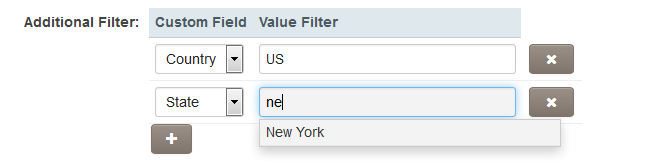
The Additional Filter setting allows you to select custom fields and associated values. These are used to filter the existing activities that will be listed within the XML. The custom fields used have to be those with pre-defined options (e.g. Combo box, Check Boxes, Dynamic Control, Ajax Lookup).
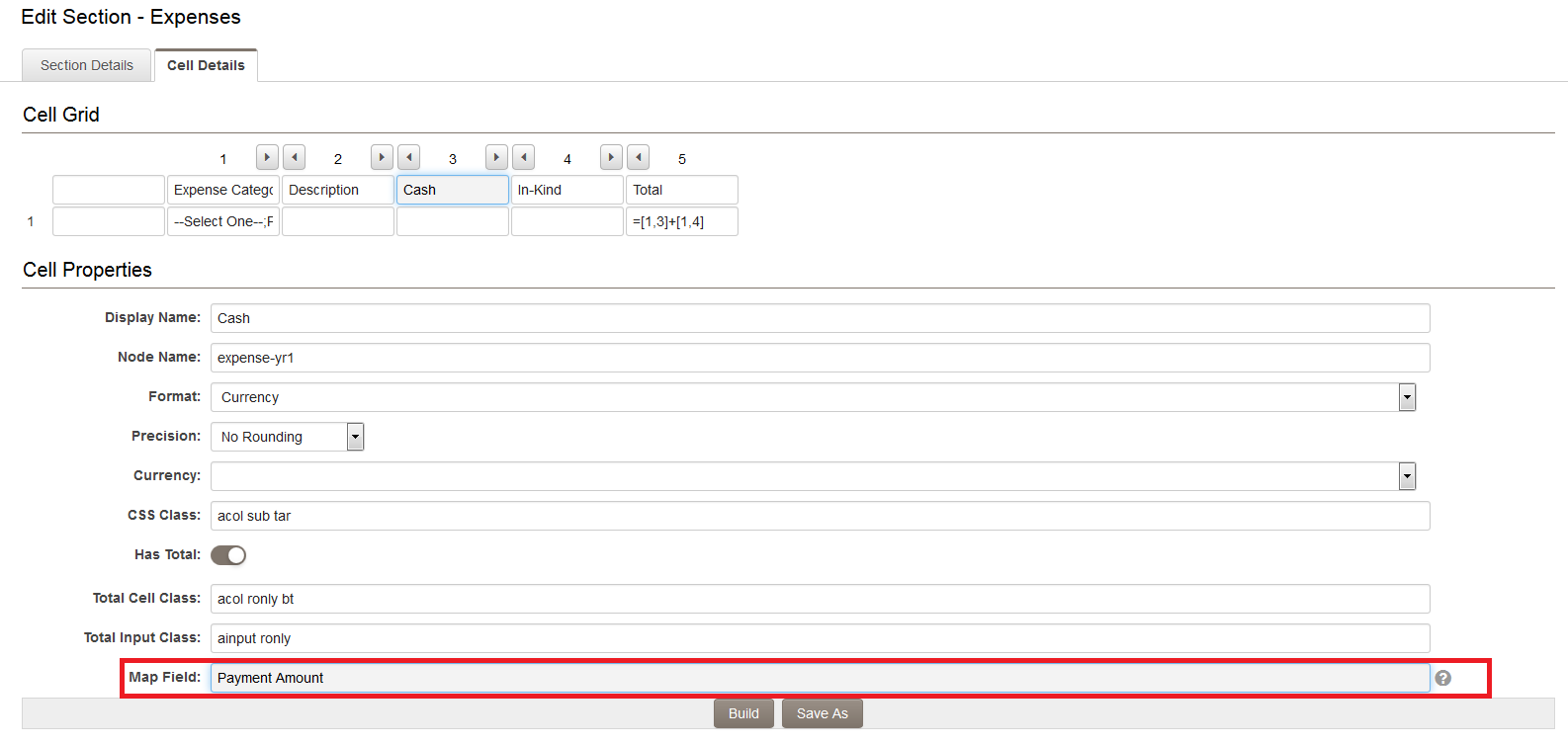
When building your section, you will need to map the fields on the Level 2s that will be referenced by the XML section.
For each Section column, enter the field name from the Level 2 type that you have selected from the Activity Type dropdown in the Map Field section:
The syntax for the Map Field section is:
- for custom fields, simply the field name (i.e., Fund Name);
- for standard fields, use the prefix sf_ and then the system name for the standard field (i.e., sf_status).
- see Standard Level 2 Field List article for a list of system names for Level 2 standard fields.
If the Standard or Custom field has a limited number of pre-defined options then these need to be defined in the Content section of the cell properties.
You may need to reference some standard field options using both the displayed name and stored ID values.
When this section is added to the XSL Template of your XML field, the list of Level 2 activities will be displayed when the XML is opened. Level 2s can be added, deleted and modified directly from the Level 1 XML field.
Displaying XML Data
Displaying XML Data on an object
The XML custom field opens in a modal window and the user must click a button to launch the modal window and see the information entered. You can however, display the information entered into a Special - XML Data custom field on your object, such as a grant application, without requiring the user to click a button and launch the modal window. To do this we use the Read Only – System Variables custom field. The same syntax can be used elsewhere in the system (e.g. include Display Only - Web Page View, Special MS Word Merge, visibility conditions, etc.) when referencing the xml values.
- Go to the desired location where you want to create the custom field.
- Click the New Field (+) button in the action bar.
- For Field Type select Read Only – System Variables.
- Enter a Field Name.
- For Variables enter @xml.CustomFieldName.SectionNodeName.html@ (replace the CustomFieldName and SectionNodeName with the actual names from your XML).
- Scroll Down to the Display section.
- For Caption select Hide Caption (we recommended that you hide the caption for the display so that you can utilize the full screen width).
- Click Save.
- Navigate back to the XML custom field and click Save (Display Fields Refreshed Upon Edit will be updated with the custom field ID of the Read Only we just created. From now on when a user edits the XML the read only will be automatically updated. If you miss this step it will only refresh when the object is saved).
Access, Display and Format options for XML Data
The syntax options for accessing, displaying and formatting the data from the XML fields are detailed below.
- Extract the value from a specific individual cell using the field name.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnnodename@
- Extract the value from a specific individual cell using the field id.
@xml.#fieldid#.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnnodename@
- Extract numeric value and return in comma format (i.e. 1000 will display as 1,000).
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~comma(columnnodename.nodevalue)~ #]@
- Extract a numeric value and return in currency format.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~currency(columnodename.nodevalue)~ #]@
- Extract a numeric value and return in a specific currency format.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~currency_eur(columnodename.nodevalue)~ #]@
Further currency formatting options below
| usd | $300.00 |
| eur | €300.00 |
| jpy | ¥ 300 |
| zar | R 300.00 |
| inr | ₹300.00 |
| frca | 300,00 $ |
- Extract a numeric value and return in currency format with two decimal places. If pulled from a dynamic XML section then you will see multiple values.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~currency_eur(columnodename.nodevalue,2)~ #]@
- Extract a value and return the number of characters in the field.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnodename.nodevaluelength@
- Extract a numeric value and return in currency format with two decimal places for value pulled from a static XML section.
<!--@sscalculation(format("@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.columnodename.nodevalue@",2))-->
- Extract a percentage value and format with two decimal places. If pulled from a dynamic XML section then you will see multiple values.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~percentdisplay(columnodename.nodevalue,2)~ #]@
- Extract date values and return with specific formatting using the following syntaxReturn the date in the user's date format
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.formatdate(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Return the year.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.year(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Return the month.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.month(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Return the month name.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.monthname(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Return the day.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.day(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Return the day of the week.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.dayweek(columnnodename.nodevalue)@
- Count the number of rows the user created in a dynamic XML section.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.nodecount@
- Return the XML feed (code) from the field.
@fieldname.xmlvalue@
- Return multiple rows for XML with dynamic sections.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# ~columnnodename.nodevalue~ #]@
- Return Filtered row values for XML with dynamic sections.
@xml.fieldname.sectionodename.rownodename[#(?criteria="~colunnnodename.nodevalue~" == "matching criteria")~columnnodename.nodevalue~ #]@
- Return multiple rows for XML with dynamic sections in a custom html table.
<table> <tbody> @xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename[# <tr> <td>~columnodename.nodevalue~</td> <td>~columnodename.nodevalue~</td> <td>~columnodename.nodevalue~</td> </tr> #]@ </tbody> </table>
- Return a single value in the total row of a Dynamic XML.
@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.rownodename.total.columnnodename.nodevalue@
Styling XML data for web and print (PDF)
If you enable the Section Builder and Apply Default Styles is enabled in each section of your XML custom field, the field will be automatically styled. If you have manually added CSS classes to your cells, you will need to remove those classes and check Apply Default Styles again and then click Build on your XML in section builder.
Administrators with CSS knowledge can modify the look and feel of their XMLs (e.g. make columns wider or thinner). To modify the look and feel of your XML, create an external CSS style sheet, upload the style sheet to a SmartFolder, add classes to the elements in your XML, and add a link to the style sheet in your Special - XML Data or Read Only - System Variable custom fields.
Styling XML Data for Printing
You can print your XML if you are displaying it in a Read Only - System Variable. Size your your XML to fit within 700 pixels wide (portrait) or 900 pixels wide (landscape) to avoid content cutting off, when a PDF is generated. If you have more than one section and more than a few columns, some of your content may cut off when printed if it is not sized. You will also notice columns between sections do not align. To fix this, we will use CSS in a SmartFolder and amend our Read Only - System Variable, which is displaying the XML information.
Wrap the content in your read only system variable with a div and give the div a class. We do this to control the width. Wrap the section syntax in a div and give it a class. We do this so we can control the size of cells and the fonts. e.g.
<div class="xml700"><div class="xmlTitleBar">Title Bar Name</div><div class="xml3col">@xml.fieldname.sectionnodename.html@</div></div>
Now create a CSS file. e.g.
@charset "utf-8";
/* CSS Document */
.LeftAlign {text-align:left;}
.RightAlign {text-align:right;}
.xml700 {width:700px;}
.xml3col .xmlLabel {width:470px; min-width:470px; max-width:470px;}
.xml3col .xmlCell {width:80px; min-width:80px; max-width:80px;}
.xml3col .xmlCell.note {width:150px; min-width:150px; max-width:150px;}
Go to the desired SmartFolders and upload your CSS file. Use View URL to get the path to the CSS file. Then add the relative link back into your Read Only - System Variable. e.g.
<link href="/files/427076/f114840/filename.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" />
Add the class RightAlign to the desired cells in the section builder.
If you want to make one cell larger than the others, add a custom class to that cell in the section builder e.g.
.xml3col .xmlCell.note {width:150px; min-width:150px; max-width:150px; font-size:12px}
I can add note to a cell that has xmlCell in a section wrapped in a div with a class xml3col and that cell will become 150 pixels wide.
Note: your cells must add up to 700 pixels if you are displaying your budget in a portrait PDF on letter size paper (8.5 x 11”).
Using different styles for Print and Web with XML Data
You can have one look for your XML when it is onscreen and another when it is in PDF format for printing. To do this, create two Read Only - System Variables custom fields, create two CSS style sheets in SmartFolders and reference the desired style sheet in the desired Read Only - System Variables. Then on the Read Only - System Variables for viewing on screen for SmartFields View choose Exclude. This custom field will no longer be included in PDFs generated using the SmartFields variable. For the other custom field you want to print, choose Only display for SmartFields View. Now one Read Only - System Variables will appear on screen and another when the PDF is created, and you can have a separate style sheet to control the look and feel of both.
Reporting on XML data
Extract XML value in a report using the following syntax in the report builder. This will return one value for static XML sections specific to the row and multiple values for Dynamic XML sections across all rows.
ExtractValue([this], '/worksheet/sectionnodename/rownodename/columnnodename')
Appendix
Field options and settings
General Settings
Custom Field ID: Used internally to reference the user's input.
Field Type: Used to select the field type from list of available field types.
Field Name: Used internally to reference the user's input.
Description: Used for a general description, this field only appears on the configuration page.
XSL Template: Used to define how the XML will look.
XML Tag Mapping: Used to Tag Maps.
XML Javascript Function: Used for JavaScript and jQuery functions such as validations.
Show View XML Button: Used to display the XML button. This button opens the xml feed (code) in a new window.
Show Upload Button: Used to display the upload button. This button enables the user to upload an XML, and if the node structure matches that of the field, it will populate the cells with the correct values.
Show Up/Down Button: Used to display an up and down arrow on each row of a dynamic XML section. Enabling the user to move rows up and down.
Show Clear Button: Used to display the Clear button on the XML field. Enabling the user to quickly clear all values from the XML form.
Display fields refreshed upon edit: Displays the ID of custom fields that reference this field. When this field is modified the references will automatically update.
Custom Field Ids: Used to reduce variable processing time. Specify field ids of custom fields referenced from within the current field.
Display
Display Order: Used to define where this field appears relative to other fields. Lower numbers appear closer to the top of the page.
Tab Name: Used to display the field under a specific tab.
Caption: Used as a label or question before the field. If left blank, the Field Name will be displayed as the caption.
Caption Location: Used to control the position and visibility of the caption. See Examples Label_Display_Options
Instructions: Used to display text in the caption area. Instructions appear below the caption and are always visible unlike tool tips that appear on mouse over.
Button Label: Used to specify the text that appears on the button. You can also specify an icon.
Tool Tip: Used to display a text message when the user hovers over the question mark. These messages are intended to assist the user in filling in the desired field.
- On New Record: Used to control when the field should be displayed.
Options
Appear Mandatory: Used to make the field look like it is required without doing validation. This is used in conjunction with other validation methods such as SmartCheck, Submit Logic or Browser Script.
Track Changes: Used to log changes to the field e.g. who updated the field when and what was the new and old values.
Enable Builder: Used to create sections, define rows, columns, formulas and styles in your XML.
Enable KML: Used to upload a KML file which is used to display geographic data on a map.
Disable Field from Global Search: Used to control the display of this field in the global search results.
Value Storage
Value Storage: Used to save values to another field on the same entity.
Example of XML field
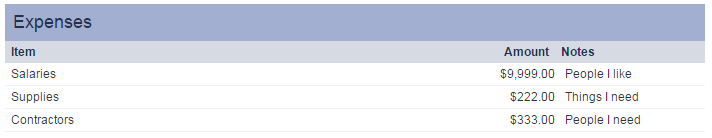
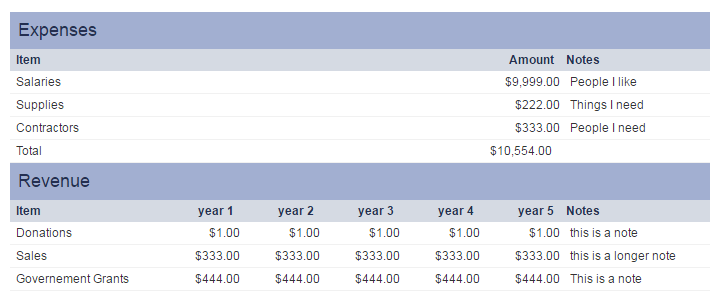
Here is an example of an XML field with one section (Expenses) 3 static rows (Salaries, Supplies and Total) and 3 columns (Amount, Notes and Date).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <worksheet> <Expenses> <Salaries> <Amount>50000</Amount> <Notes>People I work with</Notes> <Date>2016-11-30</Date> </Salaries> <Supplies> <Amount>30000</Amount> <Notes>Things I need</Notes> <Date>2016-11-30</Date> </Supplies> <Total> <Amount>8000</Amount> <Notes></Notes> <Date>2016-11-30</Date> </Total> </Expenses> </worksheet>