Difference between revisions of "Single Sign-On"
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
* "Unique Identifier Field (UID)" is used to identify the user account and needs to be an attribute that is unique to each user in SmartSimple. This needs to be an attribute common to both the SmartSimple and the client-side system (typically e-mail address or employee ID) | * "Unique Identifier Field (UID)" is used to identify the user account and needs to be an attribute that is unique to each user in SmartSimple. This needs to be an attribute common to both the SmartSimple and the client-side system (typically e-mail address or employee ID) | ||
* "X509Certificate (SAML2 Only)" is the signing certificate to be provided by the client. The formatting of this should be the certificate value without the "begin certificate" and "end certificate" header and footer lines. Also, depending on how the client-side system sends this value within the SAML assertion the certificate value will typically be formatted to just a single line but could also be multiple lines and so must be entered into SmartSimple in the same format | * "X509Certificate (SAML2 Only)" is the signing certificate to be provided by the client. The formatting of this should be the certificate value without the "begin certificate" and "end certificate" header and footer lines. Also, depending on how the client-side system sends this value within the SAML assertion the certificate value will typically be formatted to just a single line but could also be multiple lines and so must be entered into SmartSimple in the same format | ||
| − | * It is also recommended to disable the Session Timeout Alert setting | + | * It is also recommended to disable the Session Timeout Alert setting within the Global Settings -> Security section as that feature would not be applicable to users logged in through single sign-on |
===SSO Configuration in Client-Side System=== | ===SSO Configuration in Client-Side System=== | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 2 June 2017
General Information
SmartSimple provides Single Sign-On (SSO) integration through SAML 2.0
Implementation of SSO requires configuration both within SmartSimple and within the system that will provide the authentication.
SmartSimple's implementation of SSO acts as the Service Provider and assumes the client has the infrastructure and resources to host, configure, and manage the Identity Provider service. Please contact your account manager or SmartSimple Support for further information.
SAML 2.0
SmartSimple supports SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) 2.0 as the Service Provider through our own proprietary implementation of this standard.
Only Identity Provider-initiated authentication is supported, meaning the end user will first authenticate on the client-side system/infrastructure and then be forwarded to SmartSimple. The client Identity Provider service will construct a base64-encoded SAML assertion and send this to the user's browser. The user's browser will then relay this assertion to the SmartSimple server for SSO authentication.
Prerequisites
- You must provision your own Identity Provider service, third-party or otherwise, for use with this feature. Enabling and maintaining the Identity Provider is your responsibility
- You must provide SmartSimple with a public key in base64-encoded X.509 Certificate format for digital signature validation
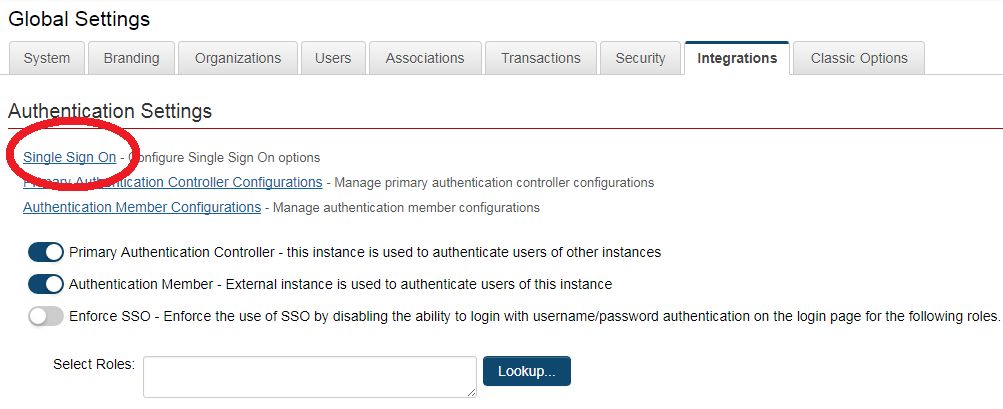
SSO Configuration in SmartSimple
Within SmartSimple, SSO settings are accessed through the Global Setting, Connectivity tab.
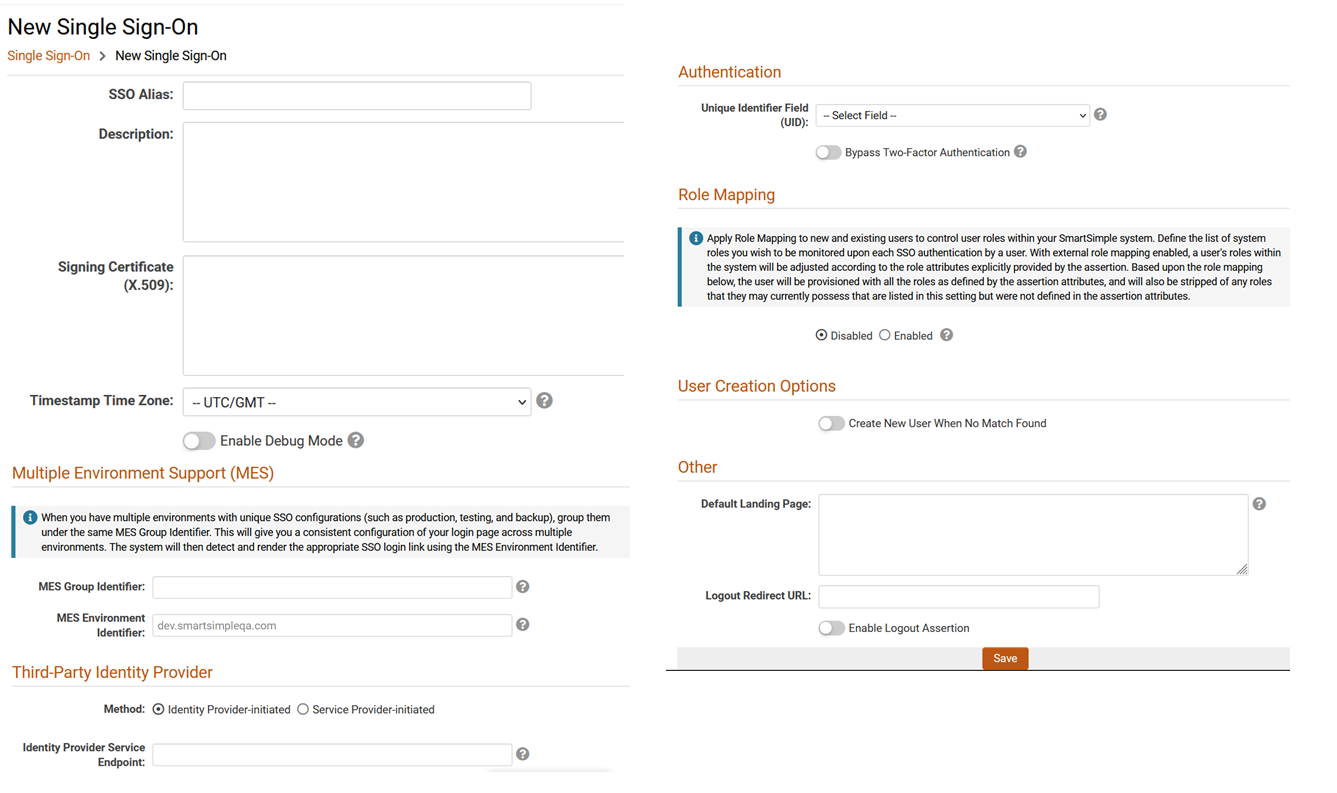
- "SSO Alias" is used to identify the SSO connection and should be configured by default to be 'SAML2'. If multiple SSO connections are to be configured then you may include an additional <Attribute> element on the client-side assertion named 'SSOModule' to specify the SmartSimple connection by matching a unique "SSO Alias" value
- "Unique Identifier Field (UID)" is used to identify the user account and needs to be an attribute that is unique to each user in SmartSimple. This needs to be an attribute common to both the SmartSimple and the client-side system (typically e-mail address or employee ID)
- "X509Certificate (SAML2 Only)" is the signing certificate to be provided by the client. The formatting of this should be the certificate value without the "begin certificate" and "end certificate" header and footer lines. Also, depending on how the client-side system sends this value within the SAML assertion the certificate value will typically be formatted to just a single line but could also be multiple lines and so must be entered into SmartSimple in the same format
- It is also recommended to disable the Session Timeout Alert setting within the Global Settings -> Security section as that feature would not be applicable to users logged in through single sign-on
SSO Configuration in Client-Side System
The elements required for setup of the client-side identity provider connection are listed below.
- Unique user identifier. Within the SAML assertion, this value can be sent in the standard <NameID> element, or optionally within an <Attribute> element named 'UID'
- Assertion Consumer Service URL. This will be equal to '/SAML2/' appended to your SmartSimple instance URL, e.g. https://alias.smartsimple.com/SAML2/
- Service Provider's Entity ID. This can be equal to the same as above Assertion Consumer Service URL
- Service Provider metadata XML. This is available upon request
Active Directory Federation Services
If using ADFS refer to the below steps as related to SmartSimple for setup. Some steps unrelated to your SmartSimple configuration have been omitted.
- Add a new "Relying Party Trust"
- Select Data Source: Import the Service Provider metadata XML file obtained from SmartSimple
- Display Name: Give the trust a display name, e.g. 'SmartSimple'
- In the claim rules editor select the "Issuance Transform Rules" tab and add a new rule. The LDAP attribute should be mapped to the agreed upon user identifier and an Outgoing Claim Type of 'NameID'
- To test or use this connection you will need to use the ADFS login URL and specify the loginToRp parameter as the SmartSimple SAML entity ID, e.g. https://adfs.yourlocaldomain.com/adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.aspx?loginToRp=https://alias.smartsimple.com/SAML2/. To create an automatic redirect into SmartSimple you will need to have RelayState enabled in ADFS and can then begin using a RelayState parameter to achieve this, e.g. https://adfs.yourlocaldomain.com/adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.aspx?RelayState=RPID%3Dalias.smartsimple.com%26RelayState%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Falias.smartsimple.com
Optional Information
The following optional attributes can be used in the assertion:
- UID (can be used instead of NameID as the user identifier)
- First name
- Last name
- Department
- Roles (comma delimited list of SmartSimple user roles (by name) to be assigned to the user)
- Language
- RedirectURL
SAML Assertion Example
The following is an example of a SAML Assertion :
<?xmlversion="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<samlp:Response xmlns:samlp="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol" Destination="https://alias.smartsimple.com/SAML2/" IssueInstant="2014-07-12T14:17:03.063Z" ID="BYavZkuNtRHC5rEPhIAEQrys1Wb" Version="2.0">
<saml:Issuer xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion">sso:saml2:alias:stage:SmartSimple:idp</saml:Issuer>
<ds:Signature xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#">
<ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:CanonicalizationMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/10/xml-exc-c14n#"/>
<ds:SignatureMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1"/>
<ds:Reference URI="#BYavZkuNtRHC5rEPhIAEQrys1Wb">
<ds:Transforms>
<ds:Transform Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#enveloped-signature"/>
<ds:Transform Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/10/xml-exc-c14n#"/>
</ds:Transforms>
<ds:DigestMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1"/>
<ds:DigestValue>+2uvXQh+d65mNWs0G6FBf4igIxU=</ds:DigestValue>
</ds:Reference>
</ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:SignatureValue>LEOCPec/eNBMqBV7A99...</ds:SignatureValue>
</ds:Signature>
<samlp:Status>
<samlp:StatusCodeValue="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:Success"/>
</samlp:Status>
<saml:Assertion xmlns:saml="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:assertion" Version="2.0" IssueInstant="2014-07-12T14:17:03.246Z" ID="X14MvZtPaqyUjfFCbehto32uDTG">
<saml:Issuer>sso:saml2:alias:stage:SmartSimple:idp</saml:Issuer>
<saml:Subject>
<saml:NameID Format="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified">T5014CD</saml:NameID>
<saml:SubjectConfirmation Method="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:cm:bearer">
<saml:SubjectConfirmationData NotOnOrAfter="2014-07-12T14:22:03.246Z" Recipient="https://alias.smartsimple.com/SAML2/"/>
</saml:SubjectConfirmation>
</saml:Subject>
<saml:Conditions NotOnOrAfter="2014-07-12T14:22:03.246Z" NotBefore="2014-07-12T14:12:03.246Z">
<saml:AudienceRestriction>
<saml:Audience>sso:saml2:alias:stage:SmartSimple:sp</saml:Audience>
</saml:AudienceRestriction>
</saml:Conditions>
<saml:AuthnStatement AuthnInstant="2014-07-12T14:17:03.246Z" SessionIndex="X14MvZtPaqyUjfFCbehto32uDTG">
<saml:AuthnContext>
<saml:AuthnContextClassRef>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:unspecified</saml:AuthnContextClassRef>
</saml:AuthnContext>
</saml:AuthnStatement>
<saml:AttributeStatement xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="UID">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">T5014CD</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="Email">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">david@email.com</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="First name">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">David</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="Last name">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">Smith</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="Department">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">Shipping</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
<saml:Attribute NameFormat="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:attrname-format:basic" Name="Roles">
<saml:AttributeValue xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="xs:string">Clerk</saml:AttributeValue>
</saml:Attribute>
</saml:AttributeStatement>
</saml:Assertion>
</samlp:Response>
Cipher encrypted reference
Please note that this feature has been deprecated.
The SmartSimple cipher-encrypted reference SSO is accessed by passing parameters in the URL, including an encrypted token, for authentication.
Example:
- http://myalias.smartsimple.com/QryAuth/?em=2&alias=myalias&message=dnnOBh9xvqPSC9uXZFAz10Tc
URL Request Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Sample |
| em | Encryption method | 1 or 2 |
| alias | SSO alias | ssoalias |
| message | Encrypted String, encryption method is indicated by em parameter | cm90YXJ5Oztjcm1 …… |
em (1 or 2) 1 – Message is encoded by base64 only (for systems that do not support DES encryption). 2 – Message is first encrypted by "DES" using a provided key and then encoded by base64.
alias Identifies which SSO settings should be used. SmartSimple supports multiple SSO entries.
message A string composed of 11 elements delimited by two semi-colons (;;). For example, 88;;Id12345;;John;;Smith;;Contact,Internal Staff;;Toronto branch;;Canada Office;;abc@gmail.com;;Canada;;2011-11-08 12:30:00;;English
There must be no spaces between elements.
Key used: AD789034 (example only)
Encrypted Message will be: I%2BA%2B/Qb73aUmJZyP5f3/9Lm90fIguwkAgKovK0626HxbeT7cGfdZfSGyDdAybGstBwHBZgDYqc3uhgS7YTQIxzQXIfAovKCzbHLhc/Nh/AizHemadQL1SNRQeNwKz9%2B37IR%2BrwQyvR2Qlh0On8zy7cDSZYm/QKL5EmGV3g9Z%2B10=
Note: When base64 encoding results include a '+' character, please replace '+' with '%2B'
Element Position
| Element Position |
Description | Sample | Options |
| 1 | Reserved Constant | Always 88 | Mandatory |
| 2 | Unique identifier of user. If this ID is not found in SmartSimple, either a new user will be created or the request will be rejected. This is controlled by the SSO settings within SmartSimple. | Id12345 | Mandatory |
| 3 | First Name | John | *Optional |
| 4 | Last Name | Smith | *Optional |
| 5 | Comma delimited list of roles (by name) to be assigned to the user. | Contact, Internal Staff | *Optional |
| 6 | Parent Company (one level above the user's company) | Canada Office | Optional |
| 7 | Company | Toronto Branch | *Optional |
| 8 | E-mail address | abc@gmail.com | *Optional |
| 9 | Country | Canada | *Optional |
| 10 | Date Time Stamp (GMT). Login will only succeed if the server time is within +- 10 minutes of this timestamp. This is to prevent bookmarking the SSO URL and token. If the SSO settings within SmartSimple have “debug=on”, then the timestamp is ignored. | 2011-11-08 12:30:00 | Mandatory |
| 11 | Language | English | Optional |
- NOTE: Optional items listed with an asterisk are mandatory if this will result in creation of a new user (only relevant if the Single Sign-On setting “Create User” is enabled).
The 6th parameter (Parent Company) can result in changes to the organizational hierarchy. The Company (parameter 7) will be moved under the Parent Company, so this should be used with caution if this effect is not desired.
Cipher Encrypted Reference Sample Code
The following are examples of code for Cipher Encrypted Reference SSO configuration:
PHP
Sample and library: http://nl3.php.net/manual/en/mcrypt.ciphers.php
Java
No extra library required.
Sample code:
import java.security.spec.KeySpec;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
importjavax.crypto.spec.DESKeySpec;
import sun.misc.BASE64Decoder;
import sun.misc.BASE64Encoder;
/**
*
*@author User
*/
public class DESEncrypt {
/**Creates a new instance of DESEncrypt */
public DESEncrypt() {
}
public static String encrypt(String keystr,String msg)
{try{byte[] keyAsBytes = keystr.getBytes();
KeySpec myKeySpec = new DESKeySpec(keyAsBytes);
SecretKeyFactory mySecretKeyFactory =SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
Cipher cipher Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/ PKCS5Padding");
SecretKey key =mySecretKeyFactory.generateSecret(myKeySpec);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] plainText = msg.getBytes();
byte[] encryptedText = cipher.doFinal(plainText);
BASE64Encoder base64encoder = new BASE64Encoder();
return base64encoder.encode(encryptedText);
}catch (Exception e){return null;}
}
public static String decrypt(String keystr,String msg)
{try{byte[] keyAsBytes = keystr.getBytes();
KeySpec myKeySpec = new DESKeySpec(keyAsBytes);
SecretKeyFactory mySecretKeyFactory =SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/ECB/ PKCS5Padding");
SecretKey key =mySecretKeyFactory.generateSecret(myKeySpec);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key);
BASE64Decoder base64decoder = new BASE64Decoder();
byte[] encryptedText = base64decoder.decodeBuffer(msg);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(encryptedText));
}catch (Exception e){return null;}
}
}
Vb.Net Sample
Imports System.Security.Cryptography
Public Function SSOEncrypt(ByValstrkey As String,ByVal strMessage AsString)
Dim inputByteArray() AsByte = StrToByteArray(strMessage)
Dim key As Byte()
key =StrToByteArray(strkey)
Dim des As New DESCryptoServiceProvider
des.Mode = CipherMode.ECB
des.Key = key
Dim ms As New MemoryStream
Dim cs As New CryptoStream(ms,des.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write)
cs.Write(inputByteArray, 0, inputByteArray.Length)
cs.FlushFinalBlock()
Return Convert.ToBase64String(ms.ToArray())
End Function
Public Shared FunctionStrToByteArray(ByVal str As String) As Byte()
Dim encoding As New System.Text.UTF8Encoding
Return encoding.GetBytes(str)
End Function