Interactive Mode
Contents
Interactive Mode
The AI interactive mode can be enabled on organization profiles, user profiles, and UTA records. In this example, we can configure interactive mode on a UTA to streamline the application process.
Configuring Interactive Mode
As an example, we will configure the AI on a particular UTA by the following steps:
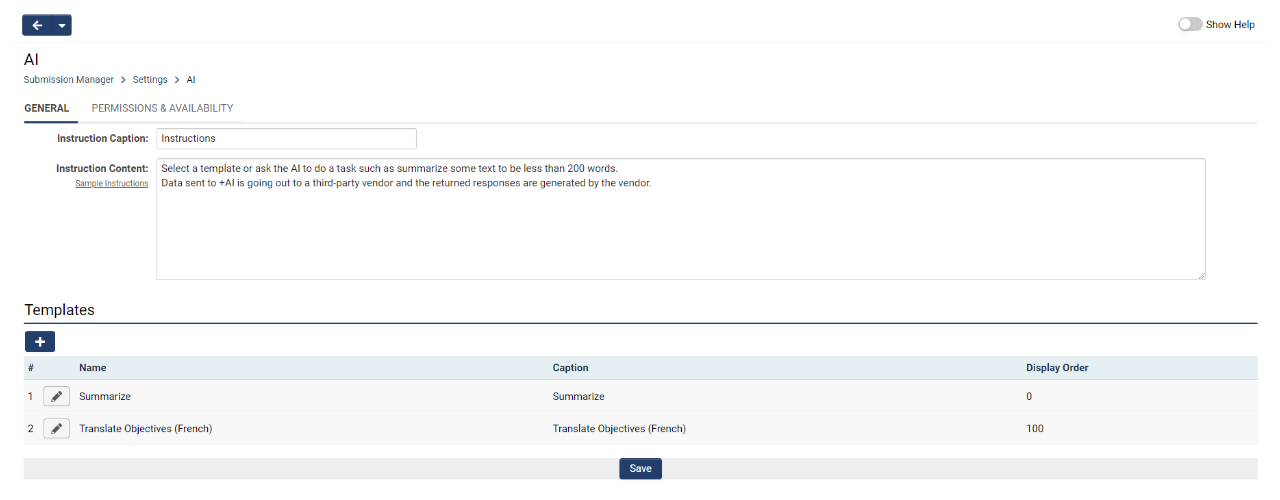
- Go to UTA > Configuration Settings > Level 1/2/3 tab > AI. On this page, custom instructions and templates can be set up.
- On the Permissions & Availability tab, set access to the feature by role, record type, or record status.
- Click Save.
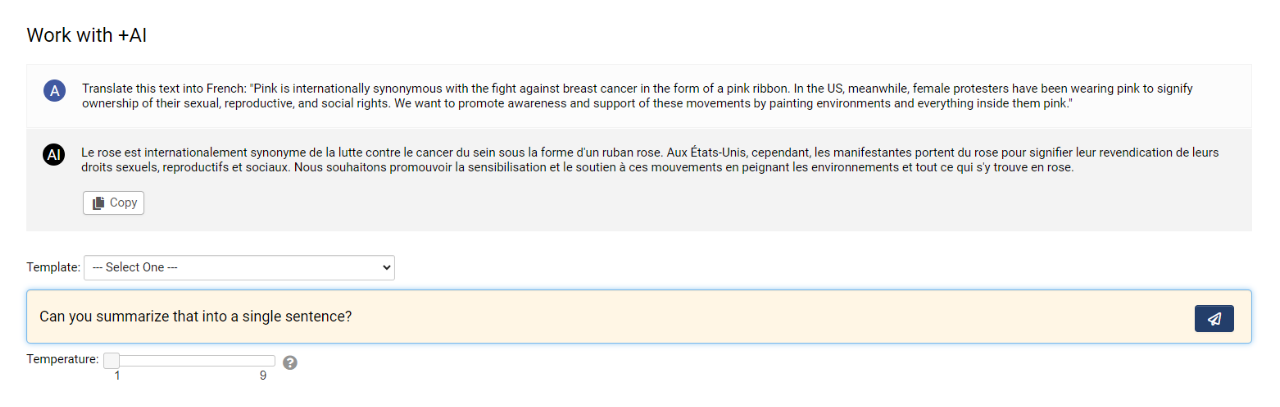
Using Interactive Mode
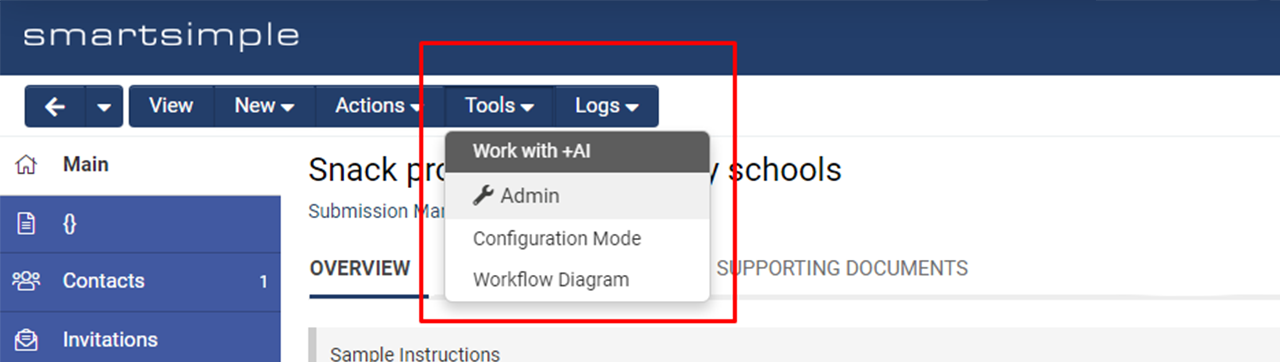
- Navigate to the desired UTA record and select Tools > Work with +AI in the top action bar.
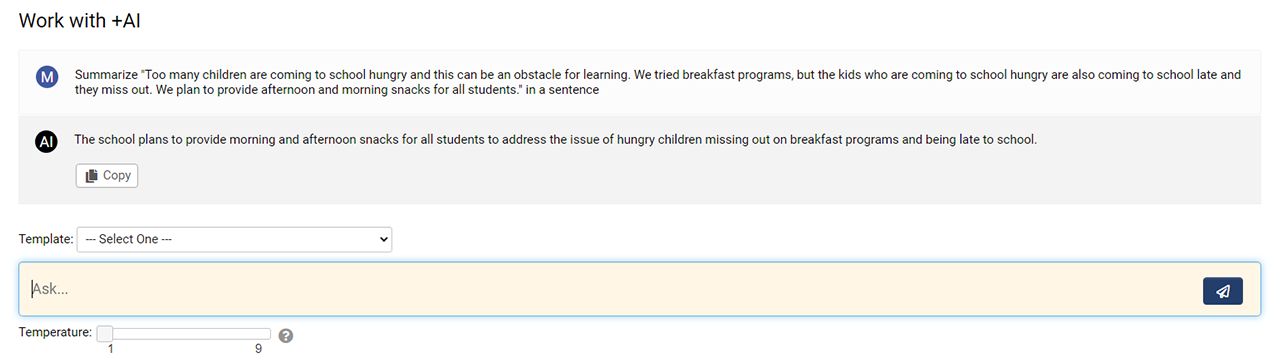
- This will open a modal window into which you can enter your prompts and adjust the Temperature setting.
Setting up Templates
Templates can be created to streamline common processes and essentially function as a prompt library. As an example, let's set up a template that will automatically translate the objectives of a record into another language. We will use a variable to achieve this goal.
Creating a Template
- Go to UTA > Configuration Settings > Level 1/2/3 tab > AI > Click the New Template button.
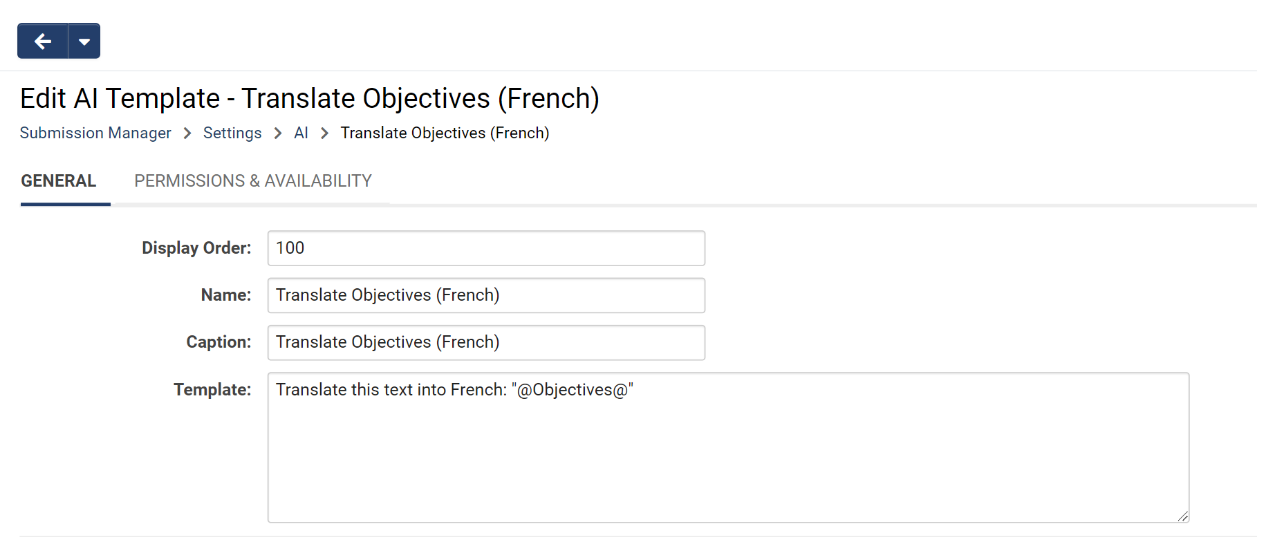
- Under the General tab, give the template a Name and a Caption. The Caption is what will be surfaced to users during template selection.
- Enter the template contents in the Template field. When referencing specific record fields, be sure to use the Field Name rather than the Caption. In our example, we can ask the AI to translate the content of a specific field into French by referencing the field name in quotations.
- Set who has access to use this template under the Permissions & Availability tab.
- Click Save.
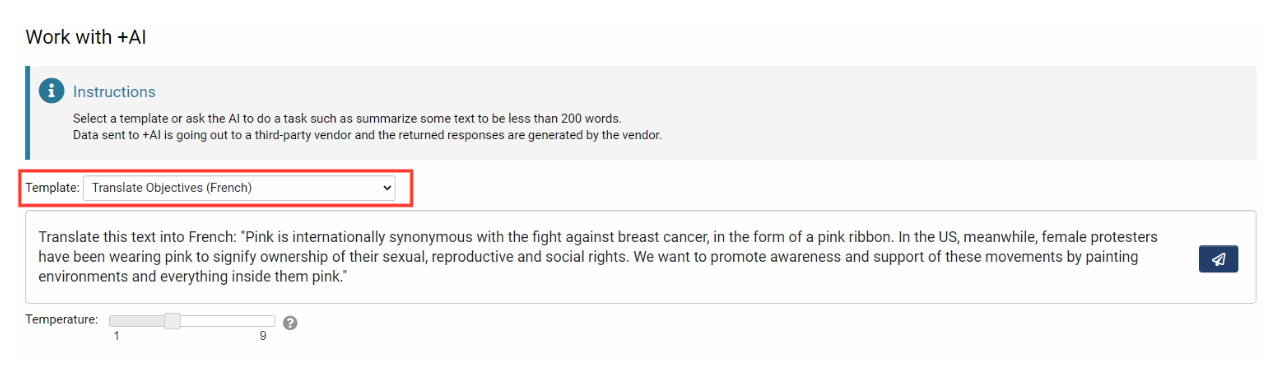
Selecting a Template
- Go to the desired UTA record > Tools > Work with +AI.
- Select the preferred template from the dropdown.
- Set the desired Temperature. This setting controls the level of randomness desired from the AI's response. A lower number correlates to a more consistent and repeatable response.
- Click the Send button. After a moment, the AI will respond to the request.
Best Practices for Template Prompts
When deciding which prompts to use in a template, it can be helpful to test the variables by going to any UTA record and clicking Tools > Configuration Mode > Variable Syntax Helper. Here, you can test your expressions and see if your variables resolve correctly.
Some best practices for prompt engineering according to OpenAI are:
- Put the instructions at the start of the prompt and use double quotation marks ( " " ) to separate the instructions from the context
- Be specific and descriptive about the desired outcome, including details about context, length, format, style, etc
- Provide an example or desired format in the prompt if necessary