SmartCheck Validation
Contents
Overview
SmartCheck Validation is a secure server side validation method. It enables custom field validation ensuring that applications and form inputs meets specified criteria and returns. It provides a better user experience than other validation methodologies and is preferred over Submit Logic. With SmartCheck, the user can see error messages in context and in one central place.
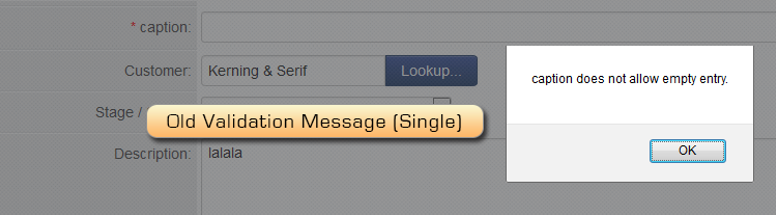
Before SmartCheck Validation, some error message would pop up individually, one after another, and some messages would appear in one box at the top, depending on how you setup your validation.
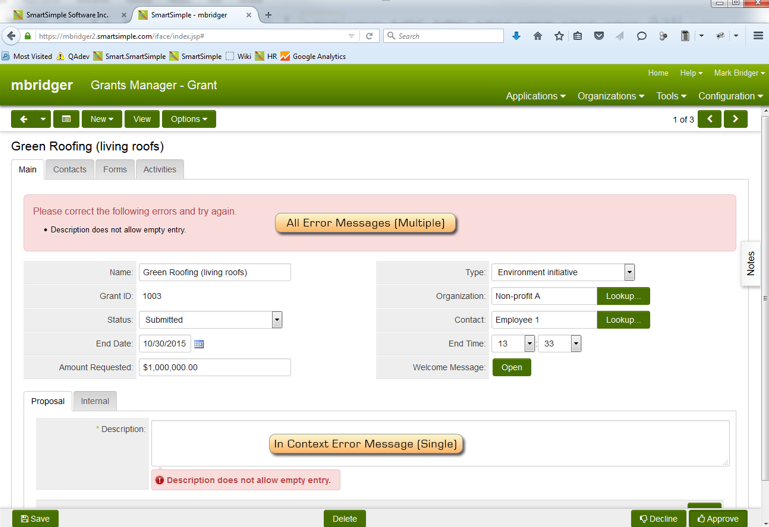
With SmartCheck Validation and the message type of Field, you will see all messages in one central spot as well as in context messages. See image below.
Clicking on an in context message, such as the description field above, enables you to temporarily hide the message. Clicking the error message at the top will bring the cursor to the field where the error is present (if there is a corresponding input).
Before you can use SmartCheck validation you must first enable it. Note that once you turn on SmartCheck Validation it is enabled everywhere. If you already set up submit logic or other validation before you turned on SmartCheck validation, you will need to test your validation to ensure it works as expected and or replace it with SmartCheck validation.
Enabling SmartCheck Validation
- In the top header, click the Configuration drop down.
- Select Global Settings.
- On the first tab called System, Check the box beside Activate SmartCheck Validation.
- Click Save.
SmartCheck Validation Structure
Each SmartCheck Validation statement shares the following structure:
- If Statement (thing to be compared)
- Result (true or false result)
- Message (to be displayed on failed result)
In the example below:
if(ssParseNum(form.getStr("cf_Store Value")) > 5)
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('Some message here');
}
Recognize the If, Result, Message structure:
if(ssParseNum(form.getStr("cf_Store Value")) > 5)
Check If the contents the of the form value (stored in the custom field named cf_Store_Value) is greater than 5,
{result.isPassed=false;
If the statement is false, set the value of the Result to "false" and print the custom message below.
result.addMsg('Some message here');
}
Form Value vs Stored Value
In the SmartCheck code builder there is a select where you choose between Form Value and Stored Value. The Form Value' is the value someone has entered into his or her application (form), this includes information that has not been saved. The Stored Value is the value from the server (information that has been saved). By using the Form Value you can validate based on information that the user has entered into the form even if they have not clicked save on their application.
Here is how it looks when you call the Form Value for a standard field:
if(form.getStr("sf_Application Name") == "")
Here is how it looks when you call the Stored Value for the same standard field:
if("@Application Name@" == "")
Notice the stored value calls the field using the variable syntax we learned in the variable processor lesson.
Field vs System Messages
In the SmartCheck code builder there is a select where you can choose between Field and System Messages. Field messages appear both at the top of the application and on the field that failed validation, this type is recommended for most validations. System messages appear only at the top of the application. You might use System messages when your validation compares more than one field, as it may not be obvious which field to highlight with the error message.
Here is how it looks when you call a system message.
result.addMsg('Your message goes here.'); }'
Here is how it looks when you call a Field message on a custom field.
'result.addMsg('cf_@field name.id@', 'Your message goes here.); }
Notice the field name is added before your message, so the system knows where to place the validation message, and the system knows where to bring your cursor should you click the message.
Examples
Check an amount is greater than $100,000
if(ssParseNum(form.getStr("cf_Amount Requested")) > 100000) {result.isPassed=false; result.addMsg('cf_@Amount Requested.id@','Amount Requested cannot exceed $100,000');
}
Application Name field black
if(form.getStr("sf_Application Name") == "")
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('Application name cannot be blank');
}
Requested Amount less than X
if(ssParseNum(form.getStr("cf_Requested Amount")) < "5000")
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('cf_@Requested Amount.id@','Field test message');
}
Number value greater than 5
if(ssParseNum(form.getStr("cf_Store Value")) > 5)
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('Some message here');
}
Single field upload field has no file
if("@Single File Field.filename@" == "")
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('Please upload a file here');
}
Multi file upload field has no files
if(ssParseNum("@level1.MUlti upload.numoffiles@") < 1)
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('Please upload at least one file'); }
Comparing two custom date fields with separate custom time fields storing 24 hour time
if(form.getStr("cf_Event Start Date")+' '+form.getStr("cf_Event Start Time") >= form.getStr("cf_Event End Date")+' '+form.getStr("cf_Event End Time"))
{result.isPassed=false;
result.addMsg('cf_@Event End Time.id@','End Time must take place after the Start Time'); }
To include other scripts into a SmartCheck script:
//@include(AnotherSmartCheckScriptName)@